
Source: National Centers for Environmental Information – National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The Significance of Spectral Irradiance in Light Source Characterization
Understanding Spectral Irradiance
Spectral irradiance, denoted by F, is a crucial parameter for characterizing a light source. It represents the power density at a specific wavelength and is measured in units of Wm-2 µm-1. Here, Wm-2 denotes the power density at the wavelength λ(µm), with m-2 indicating the surface area of the light emitter and µm-1 representing the wavelength of interest.
Relation to Photon Flux in Solar Cell Analysis
In the analysis of solar cells, spectral irradiance is often used in conjunction with photon flux. The spectral irradiance can be derived from the photon flux by converting the photon flux at a given wavelength to W/m2. This conversion involves dividing the result by the wavelength of interest. The equation for this conversion is:
F(λ) = Φ * E / λ
Where:
F(λ) is the spectral irradiance in Wm-2μm-1,
Φ is the photon flux in # photons m-2sec-1,
E is the energy of the photon in joules,
λ is the wavelength of the photon in meters.
Expressing Spectral Irradiance in Wavelength Terms
Spectral irradiance is commonly expressed in terms of wavelength for better understanding and analysis. By doing so, researchers and engineers can effectively evaluate and compare different light sources based on their spectral characteristics.
In conclusion, spectral irradiance plays a fundamental role in the characterization of light sources, particularly in the field of solar cell analysis. Understanding this parameter is essential for optimizing the efficiency and performance of photonic devices and systems.
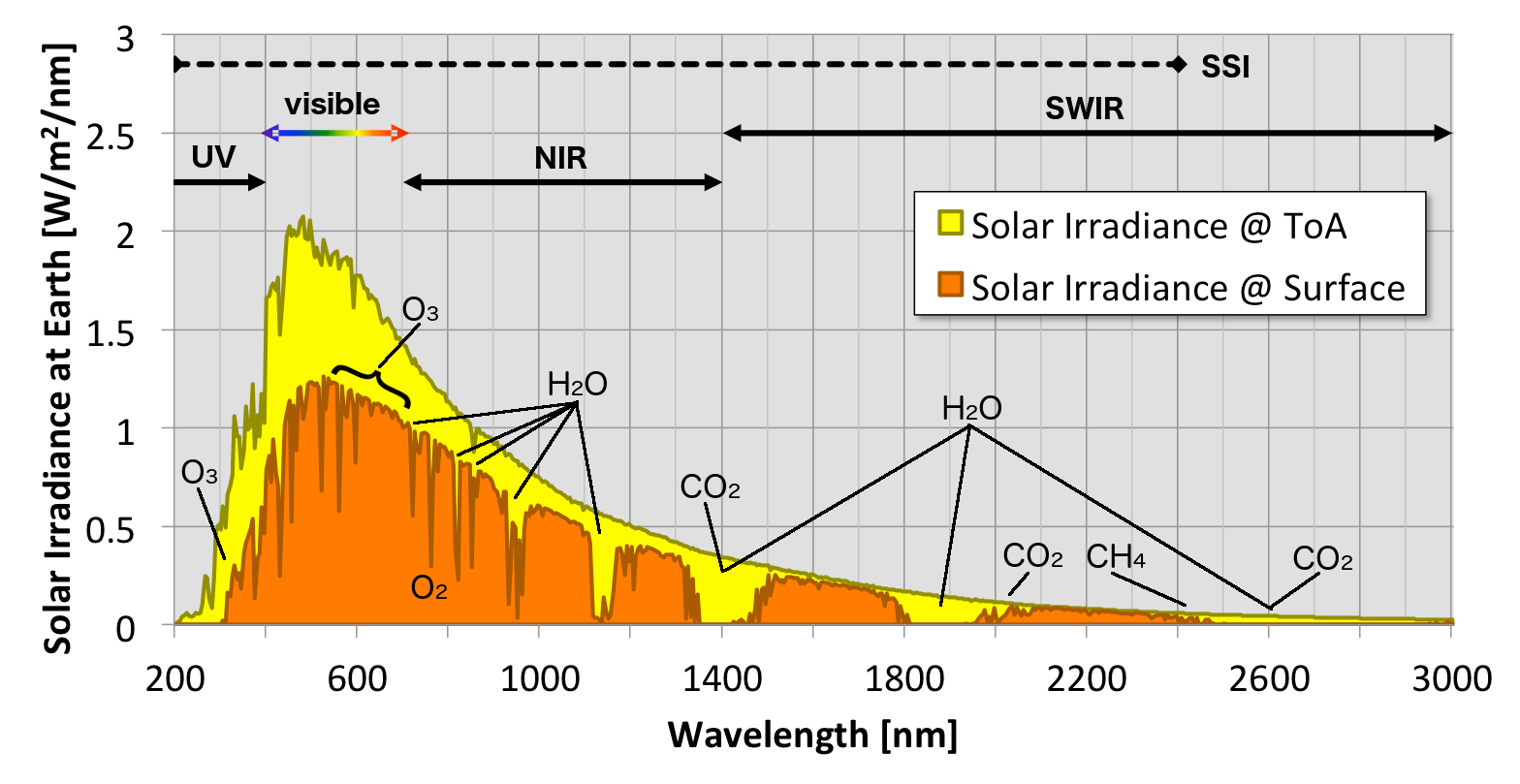
Source: Sun Climate – NASA
Feel free to comment your thoughts.
