Source: Worksheets Planet
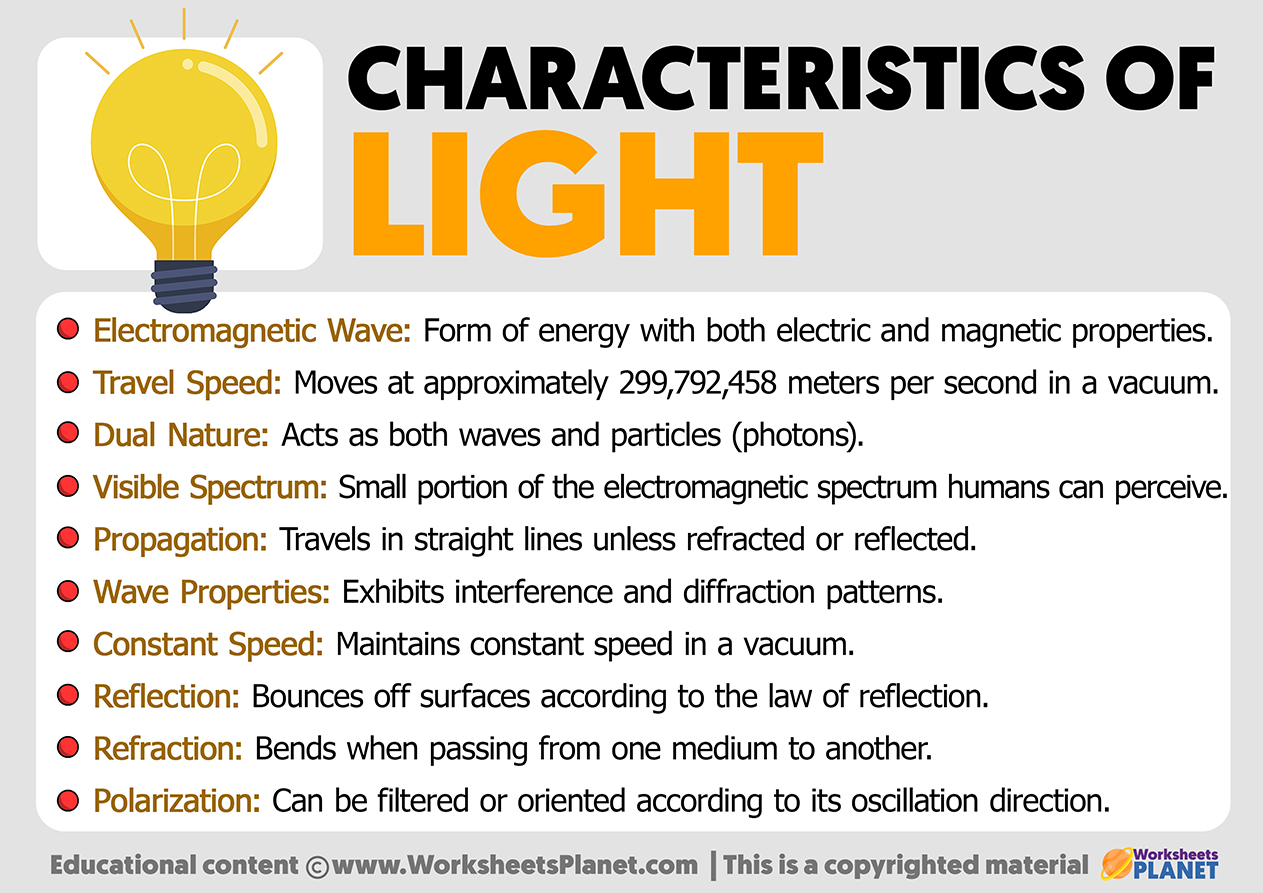
The Nature of Light
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation that is emitted by the sun. The visible light that we see is just a small portion of the entire spectrum of electromagnetic radiation.
Evolution of Light Theory
In the early 1800s, experiments demonstrated that light behaves like a wave. This wave theory gained acceptance, but in the late 1800s, discrepancies arose when trying to explain the spectrum of wavelengths emitted by heated objects. This led to the development of quantum theory by Planck and Einstein, where light is seen as consisting of energy packets called photons.
Wave-Particle Duality
Modern quantum mechanics explains that light can exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior. A photon, the quantum particle of light, can be best understood as a wave-packet. Depending on the circumstances, a photon can behave as either a wave or a particle, known as wave-particle duality.
Quantum Properties of Light
A complete understanding of light involves a quantum-mechanical analysis, as light is composed of photons. While this level of detail is not always necessary for practical applications like photovoltaics, it is essential for comprehending the fundamental nature of light.
Incident Solar Energy Characteristics
Several key characteristics of incident solar energy determine how it interacts with photovoltaic converters and other objects:
- The spectral content of the incident light
- The radiant power density from the sun
- The angle of incidence on a photovoltaic module
- The radiant energy received over time
Understanding these factors is crucial for optimizing the efficiency and performance of photovoltaic systems.

Source: YouTube
Feel Free to comment your thoughts.
