Source: YouTube
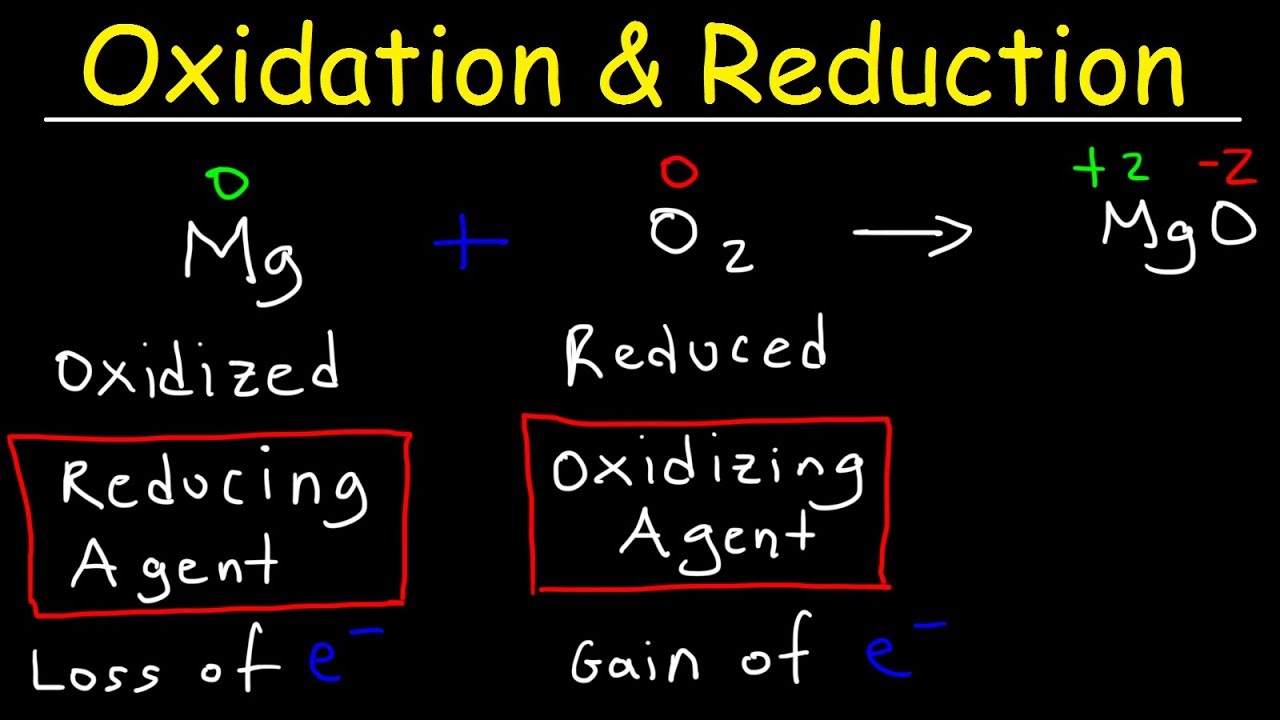
The Significance of Redox Reactions
Reduction/oxidation (redox) reactions play a crucial role in various chemical processes, both beneficial and detrimental. These reactions involve the transfer of electrons, where oxidation reactions produce electrons, and reduction reactions consume them. It is essential to note that an oxidation reaction always accompanies a reduction reaction to maintain electron balance.
Understanding Oxidation Reactions
In an oxidation reaction, a substance loses electrons, leading to an increase in its valence state. This process occurs at the anode and results in the production of electrons as one of the products. For example, when zinc metal is oxidized to form zinc ions with a 2+ valence charge, two electrons are released in the process.
Understanding Reduction Reactions
Conversely, in a reduction reaction, a substance gains electrons, causing a decrease in its valence state. This type of reaction occurs at the cathode. For instance, copper ions with a 2+ valence charge can be reduced to copper metal with a valence state of zero by accepting two electrons.
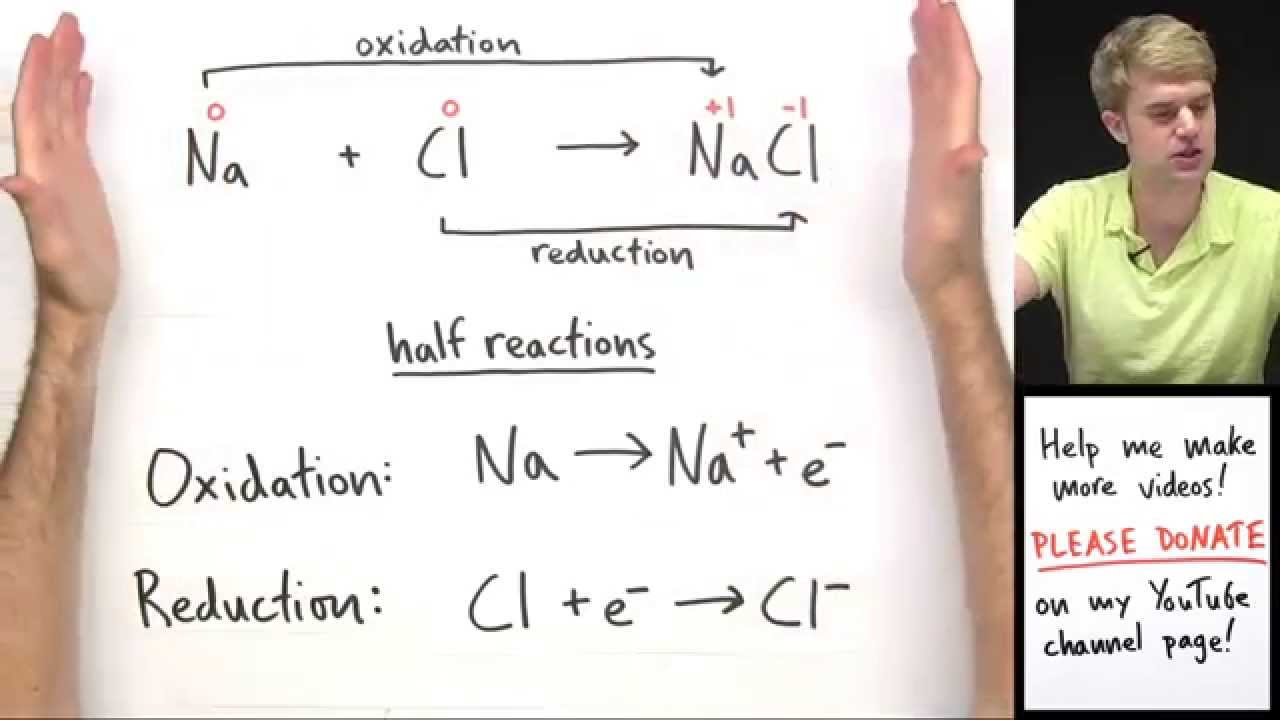
The Total Redox Reaction
When oxidation and reduction reactions occur simultaneously, they form the total redox reaction. In the case of copper and zinc, the overall reaction involves zinc acting as the reducing agent by providing electrons to reduce copper ions. As a result, zinc undergoes oxidation, while copper ions undergo reduction. It is crucial to balance not only the elements but also the electrons in redox reactions.
By understanding the significance of redox reactions and how they involve the transfer of electrons through oxidation and reduction processes, we can grasp their essential role in various chemical reactions and natural phenomena.
Source: YouTube
Feel free to comment your thoughts.
