Source: EnArgus
Optimizing Solar Cell Thickness for Enhanced Performance
When designing solar cells, achieving the optimum device thickness is crucial for maximizing efficiency. It is not simply about ensuring all incoming light is absorbed by the cell. Factors such as the diffusion length of the junction and recombination losses play a significant role. A thinner solar cell that effectively retains light absorption from a thicker device can potentially result in a higher voltage output.
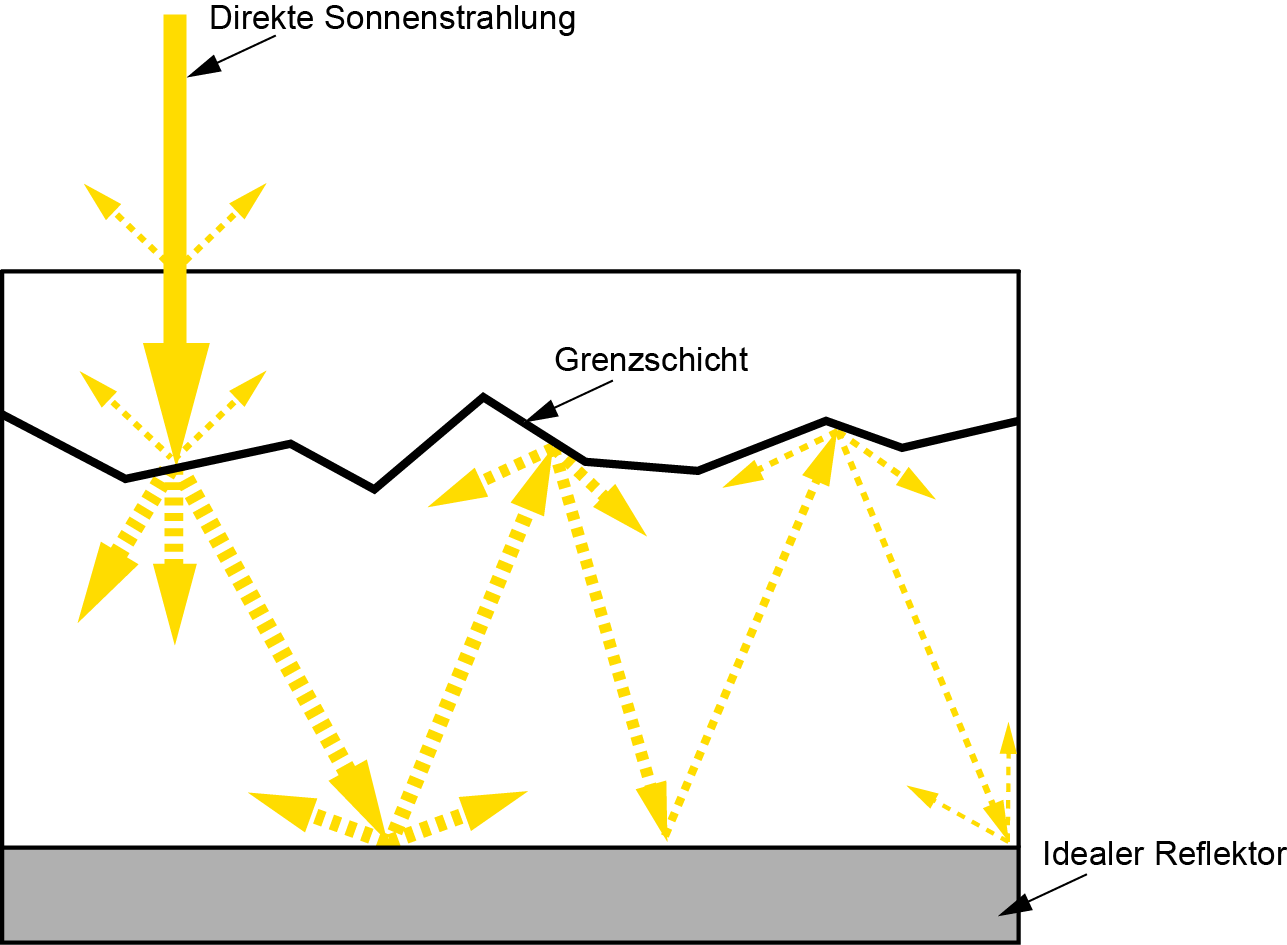
Importance of Light Trapping
An ideal solar cell structure incorporates a concept known as “light trapping.” This technique involves extending the optical path length within the cell to enhance light absorption. The optical path length refers to the distance a photon can travel within the cell before escaping. By increasing this path length, more light can be absorbed, leading to improved efficiency.
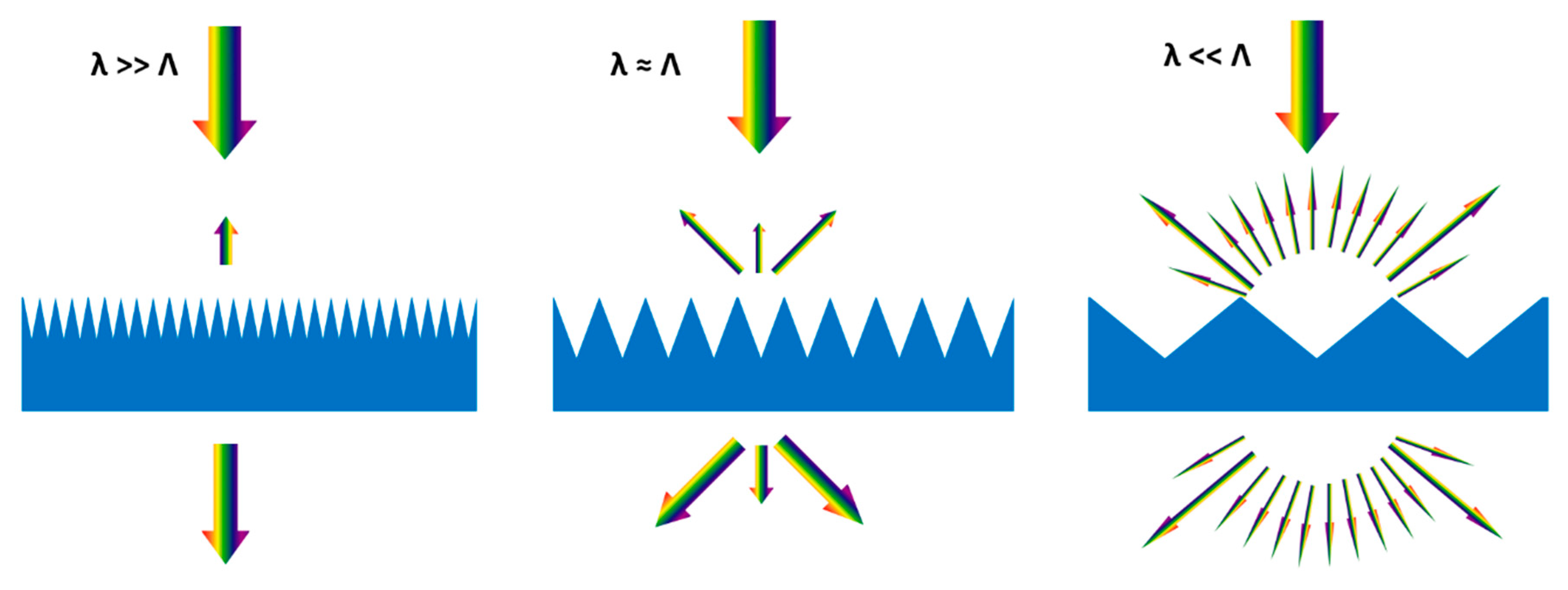
Enhancing Light Trapping Through Surface Texturing
One method to achieve light trapping is by altering the angle at which light enters the solar cell. Texturing the cell’s surface not only reduces reflection but also allows light to enter obliquely, increasing the optical path length beyond the physical thickness of the device. By leveraging Snell’s Law, which governs the refraction of light at interfaces, the angle of light incidence can be optimized to enhance trapping.
Total Internal Reflection for Enhanced Light Retention
Total internal reflection (TIR) is another phenomenon utilized to trap light within the cell. By ensuring that light undergoes multiple reflections within the cell through TIR, even thin solar cells can maintain a high optical path length. This approach enables efficient light absorption and utilization, contributing to overall performance enhancement.
Conclusion
Optimizing solar cell thickness, implementing light trapping techniques, and utilizing total internal reflection are essential strategies for enhancing the efficiency and performance of solar cells. By maximizing light absorption and retention within the cell, these methods contribute to improving the overall energy conversion capabilities of solar technology.
Source: MDPI
