Source: Reichelt · Auf Lager
Lead Acid Batteries: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Lead acid batteries are widely used in photovoltaic systems due to their long lifetime and cost-effectiveness. While they have lower energy density and efficiency compared to other types of batteries, their mature technology base makes them a popular choice for various applications.
Operation of Lead Acid Batteries
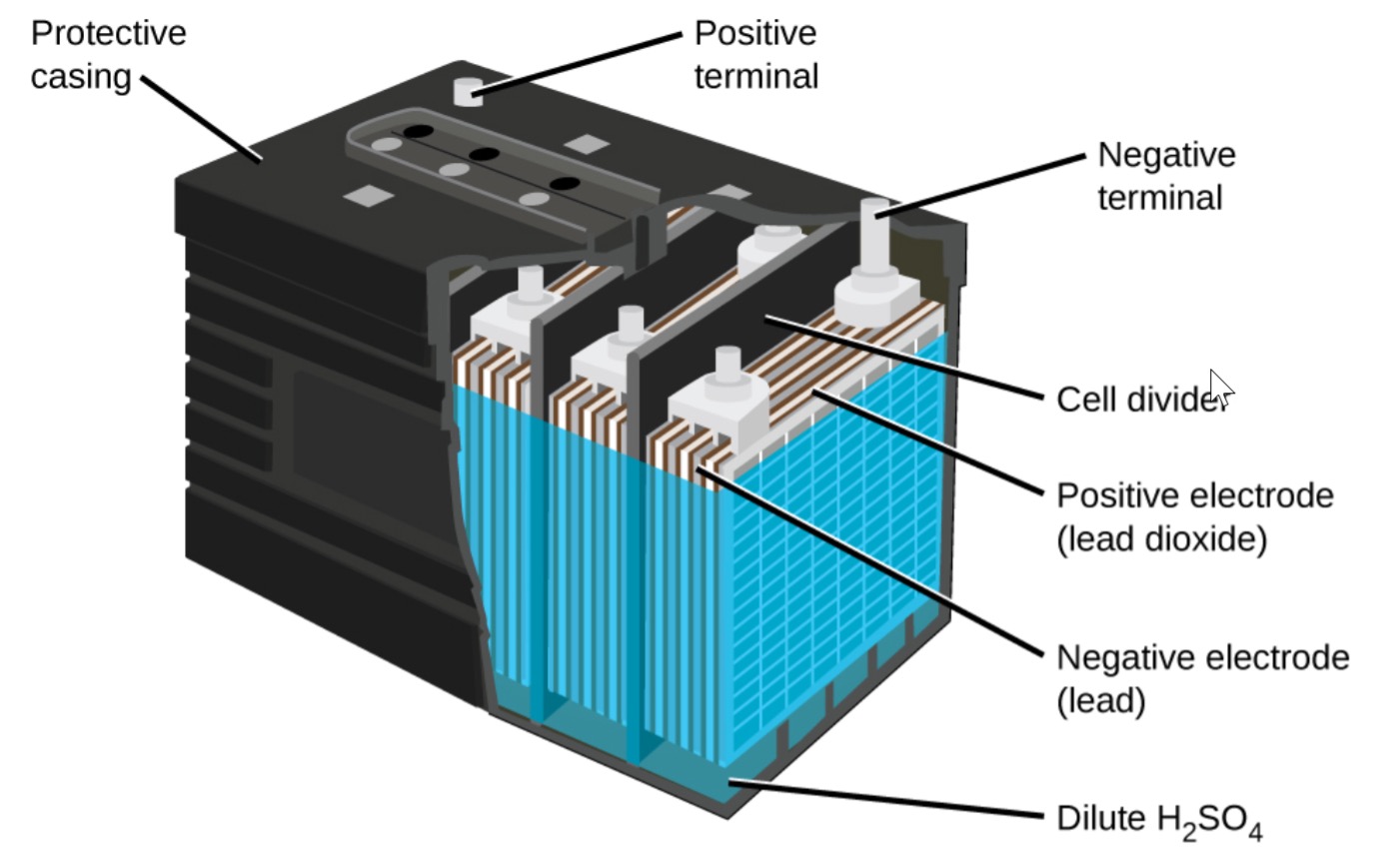
Lead acid batteries consist of negative electrodes made of porous lead and positive electrodes made of lead oxide, immersed in a sulfuric acid and water electrolyte. They store energy through reversible chemical reactions, with the formation of lead sulfate crystals during discharge.
Voltage of lead acid battery upon charging
Charging a lead acid battery involves converting lead sulfate back to lead and lead oxide, with the evolution of hydrogen gas. Overcharging can lead to gassing, water loss, and reduced battery capacity.
Characteristics of Lead Acid Batteries
Key parameters for lead acid batteries in renewable energy systems include battery lifetime, depth of discharge, and maintenance requirements. The depth of discharge impacts battery capacity and design considerations.
Battery Lifetime
Battery capacity degrades over time due to sulfation and shedding of active material. Factors like charging regime, depth of discharge, and temperature influence battery longevity.
Special Considerations for Lead Acid Batteries
Different lead acid battery configurations cater to specific requirements. Flooded batteries require maintenance, while gelled or sealed batteries offer advantages like deep cycling and lower maintenance.
Failure Modes for Lead Acid Batteries
Lead acid batteries can fail due to internal short-circuiting, open circuiting, freezing, or improper operation. Boost charging and specific gravity measurements are essential for battery maintenance.
Electrode Materials and Configuration
The choice of electrode materials and configuration impacts battery performance. Lead alloys, electrode thickness, and housing design play crucial roles in battery efficiency and longevity.
Plate Material
Lead antimony, lead calcium, and lead antimony/calcium alloys are common electrode materials in lead acid batteries, each offering unique advantages and challenges in terms of gassing, maintenance, and discharge rates.
Potential Problems with Lead Acid Batteries
Lead acid batteries may face issues like gassing, electrode damage, electrolyte stratification, sulfation, and corrosion. Proper maintenance, monitoring, and charging practices are essential to mitigate these problems and ensure optimal battery performance.
Source: BoatTEST
