
Source: YouTube
The Significance of Intrinsic Carrier Concentration in Semiconductor Materials
Understanding Intrinsic Carriers
Intrinsic carriers, namely electrons and holes, play a crucial role in the conduction of semiconductor materials. The concentration of these carriers is influenced by the material’s temperature and band gap, ultimately impacting its conductivity. Intrinsic carrier concentration is a key factor in determining the efficiency of solar cells and optimizing their performance.
Formation of Intrinsic Carriers
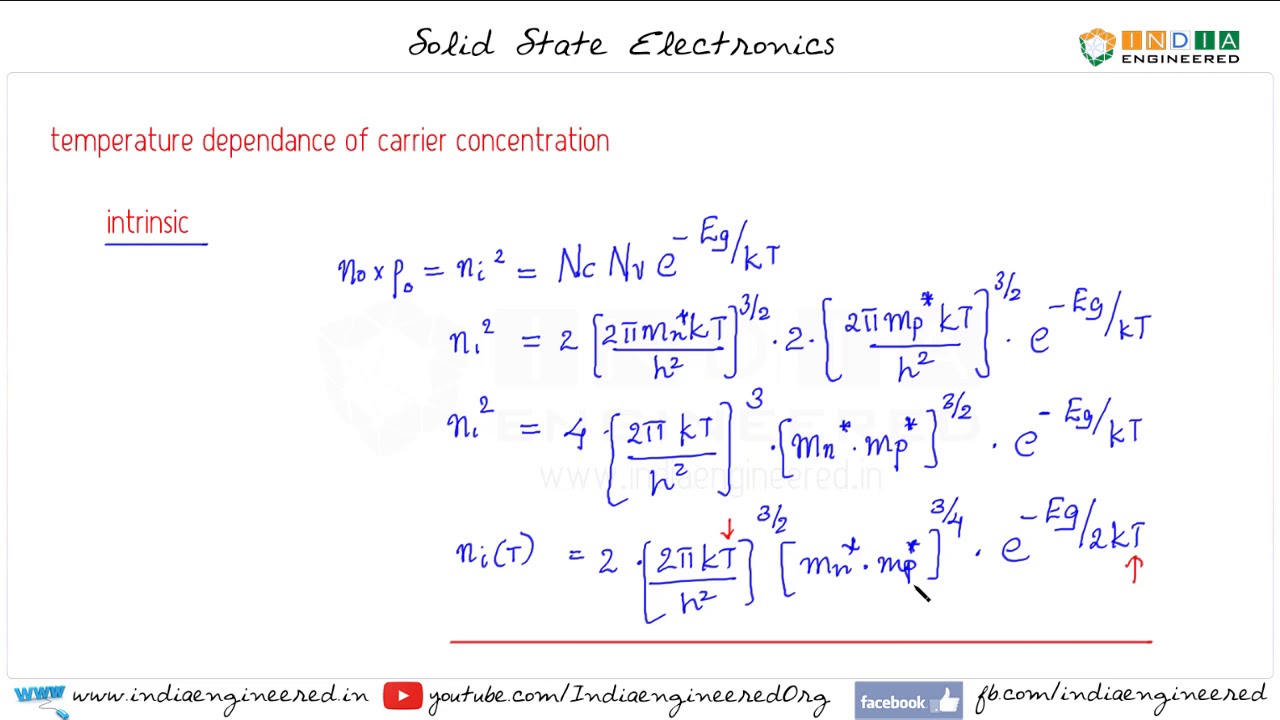
When a carrier is thermally excited from the valence band to the conduction band, free carriers are generated in both bands. The concentration of these carriers is referred to as the intrinsic carrier concentration, denoted by n i . Intrinsic material refers to semiconductor material that has not been intentionally doped with impurities to alter carrier concentrations. The number of electrons in the conduction band or holes in the valence band in intrinsic material is determined by the intrinsic carrier concentration, which is influenced by the material’s band gap and temperature.
Impact of Band Gap and Temperature
The band gap of a material affects the ease with which a carrier can be thermally excited across it. Materials with larger band gaps have lower intrinsic carrier concentrations due to the increased difficulty of carrier excitation. On the other hand, raising the temperature enhances the likelihood of electron excitation into the conduction band, leading to a higher intrinsic carrier concentration. This relationship directly correlates to the efficiency of solar cells.
Intrinsic Carrier Concentration in Silicon
Silicon, being a widely used semiconductor material, has been extensively studied to determine its intrinsic carrier concentration. At 300 K, the generally accepted value for the intrinsic carrier concentration of silicon is 9.65 x 10^9 cm-3. However, solar cells are typically measured at 25 °C, where the intrinsic carrier concentration is 8.3 x 10^9 cm-3. Various researchers have proposed formulas to calculate the intrinsic carrier concentration in silicon as a function of temperature, with minor discrepancies that fall within experimental error bounds.
Conclusion
Understanding intrinsic carrier concentration is essential for optimizing the performance of semiconductor materials, particularly in applications such as solar cells. By comprehending the impact of band gap and temperature on carrier concentration, researchers can work towards enhancing the efficiency of electronic devices and renewable energy technologies.
Source: YouTube
Feel free to comment your thoughts.
