
Source: Physics World
Solar Cell Efficiency and Design Features
Introduction
Solar cells play a crucial role in harnessing solar energy for various applications, ranging from solar cars to space missions. High efficiency solar cells are known for their superior performance, although they come at a higher production cost compared to standard silicon cells.
Design Features for High Efficiency Solar Cells
Several techniques and design features are employed in the laboratory fabrication of high efficiency solar cells to maximize their performance:
- Lightly phosphorus diffused emitters to minimize recombination losses and prevent the formation of a “dead layer” at the cell surface.
- Closely spaced metal lines to reduce emitter lateral resistive power losses.
- Very fine metal lines, typically less than 20 µm wide, to minimize shading losses.
- Polished or lapped surfaces for top metal grid patterning via photolithography.
- Small area devices and good metal conductivities to minimize resistive losses in the metal grid.
- Low metal contact areas and heavy doping at the silicon surface beneath the metal contact to minimize recombination.
- Elaborate metallization schemes, such as titanium/palladium/silver, for low contact resistances.
- Good rear surface passivation to reduce recombination.
- Anti-reflection coatings to decrease surface reflection.
Advanced Solar Cell Designs
Early solar cell designs incorporated advanced features, with two notable approaches being PERL cells and rear-contact cells:
PERL Solar Cells
The Passivated Emitter with Rear Locally Diffused (PERL) cells utilized micro-electronic techniques to achieve efficiencies of up to 25% under the standard AM1.5 spectrum. These cells featured a high-quality oxide at the front surface for reduced carrier recombination and local diffusion at the rear metal contacts to maintain good electrical contact while minimizing recombination.
An example of a solar car cell in the 1990s exhibited impressive characteristics:
- High efficiency approaching 25% under standard conditions.
- Passivated emitter for reduced surface recombination.
- Local rear diffusion at metal contacts for optimal electrical contact.
Rear-Contact Cells
Rear-contact cells, developed at Stanford University and SunPower, were another innovative design. These cells featured contacts on the rear surface, eliminating shading from the front contacts and improving overall efficiency.
Overall, advancements in solar cell design continue to drive efficiency improvements, making solar energy an increasingly viable and sustainable option for various applications.
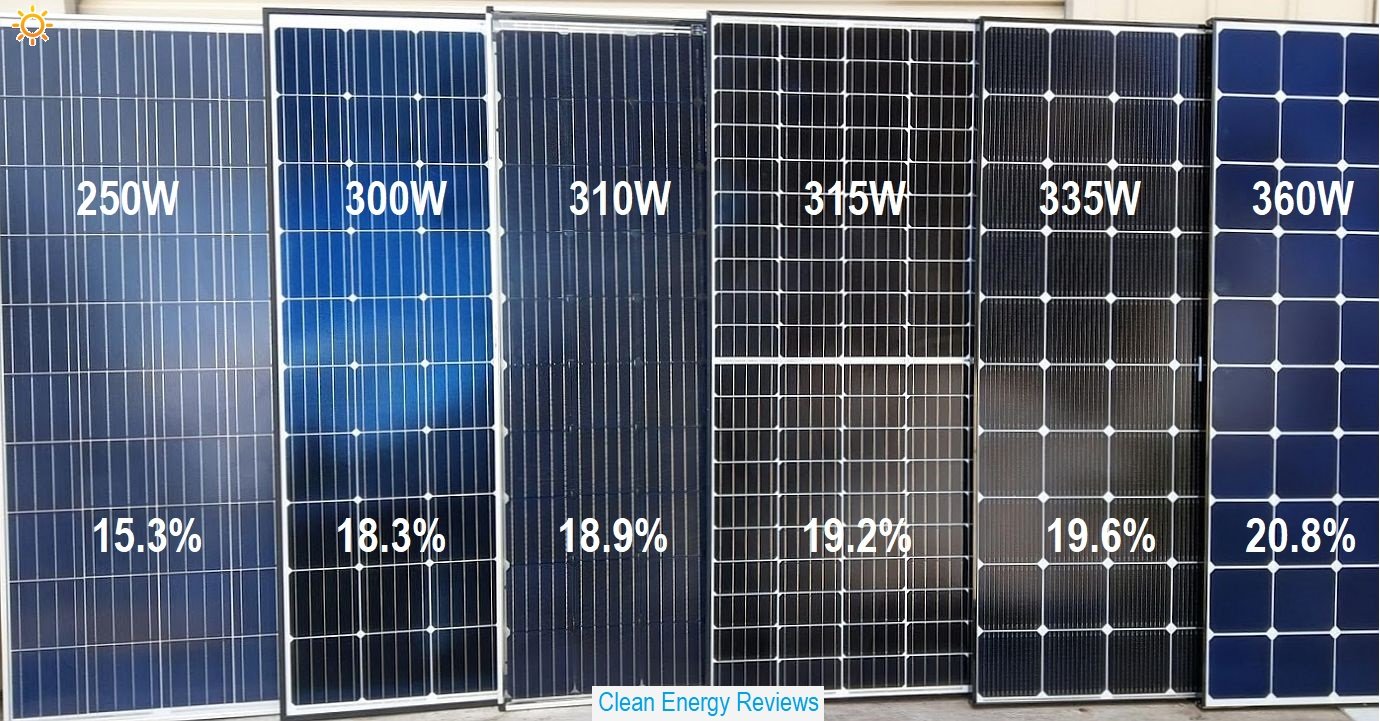
Source: Clean Energy Reviews
Feel free to comment your thoughts.
