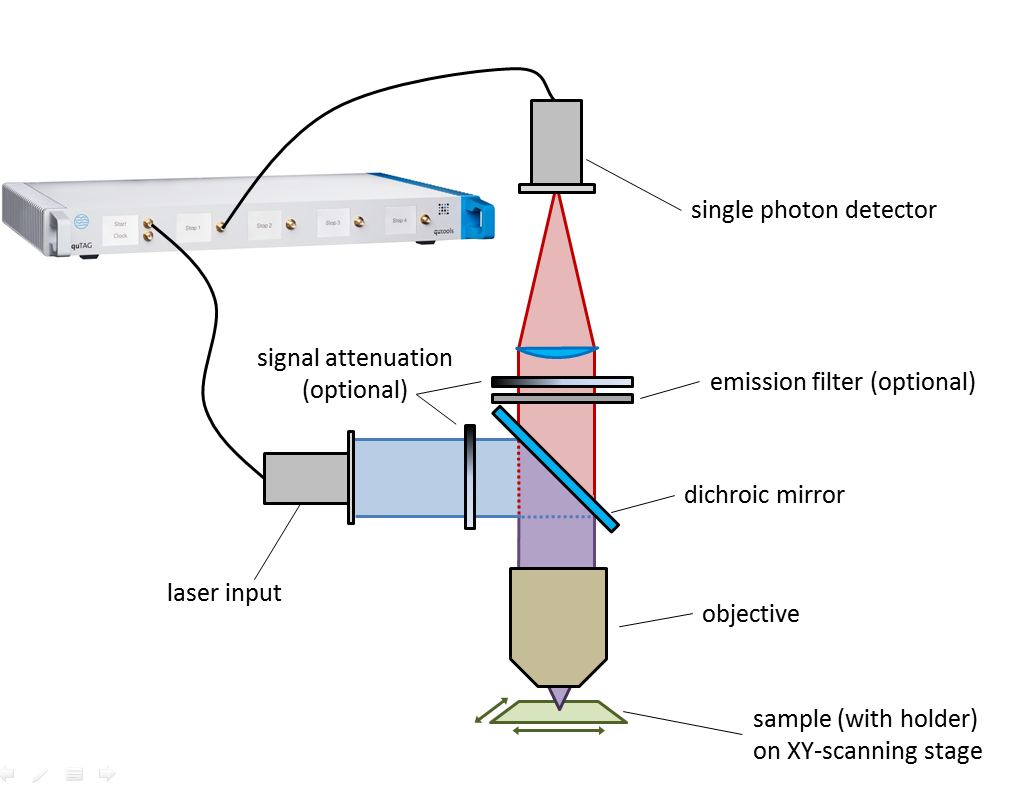
Source: qutools
The Importance of Photoconductance Decay Measurements
Understanding Transient and Quasi-Steady-State Measurements
Photoconductance decay measurements are essential for determining the lifetime of carriers in semiconductors. Two common approaches to such measurements are transient and quasi-steady-state (QSS) measurements.
Transient Measurements
In transient measurements, a pulse of light is used to excite the carriers in the semiconductor. The light is then turned off during the actual measurement, leading to a situation where the photoconductance is zero. This method allows for the study of carrier recombination dynamics in the material.
Quasi-Steady-State Measurements
Quasi-steady-state measurements, on the other hand, involve the assumption that the light illuminating the semiconductor is varying very slowly. This assumption leads to a situation where the rate of change of carrier density is negligible (d(Δn)/dt = 0), allowing for the determination of the steady-state behavior of the carriers.
Generalized Equation for Photoconductance Decay
The general equation for photoconductance decay can be applied to both transient and quasi-steady-state measurements. This equation is particularly useful when the time constants of the light pulse and the semiconductor material are similar, enabling a more accurate determination of carrier lifetime.
By utilizing both transient and quasi-steady-state measurements, researchers can gain valuable insights into the carrier dynamics of semiconductors, aiding in the development of more efficient photovoltaic devices and other semiconductor applications.
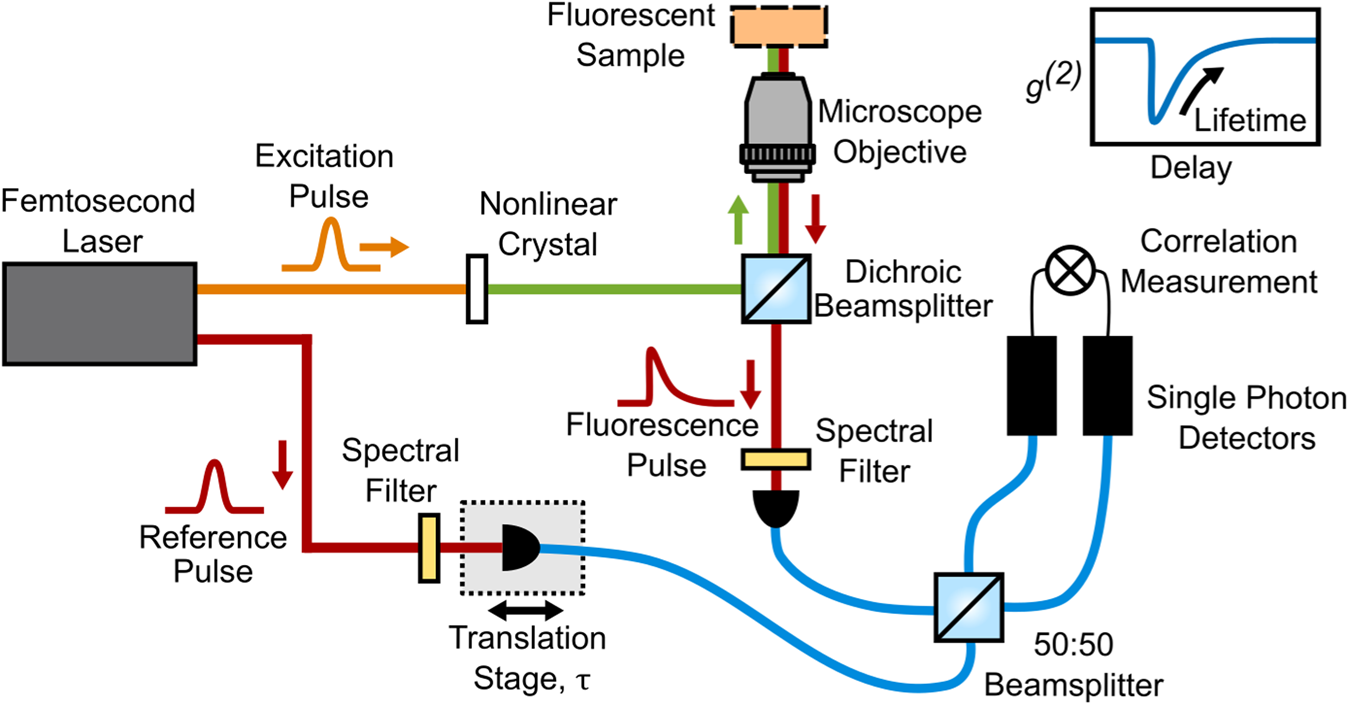
Source: Nature
