Source: Articles | Murata Manufacturing – Murata
The Science of Batteries
Batteries are essential devices that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy through a series of oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions. These redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons, leading to the generation of electrical energy.
Primary vs. Secondary Batteries
Primary batteries operate as one-time-use devices, where the chemical energy is converted into electrical energy in a non-reversible process. This means that primary batteries cannot be recharged. Common examples of primary batteries include alkaline consumer batteries found in everyday devices like flashlights.
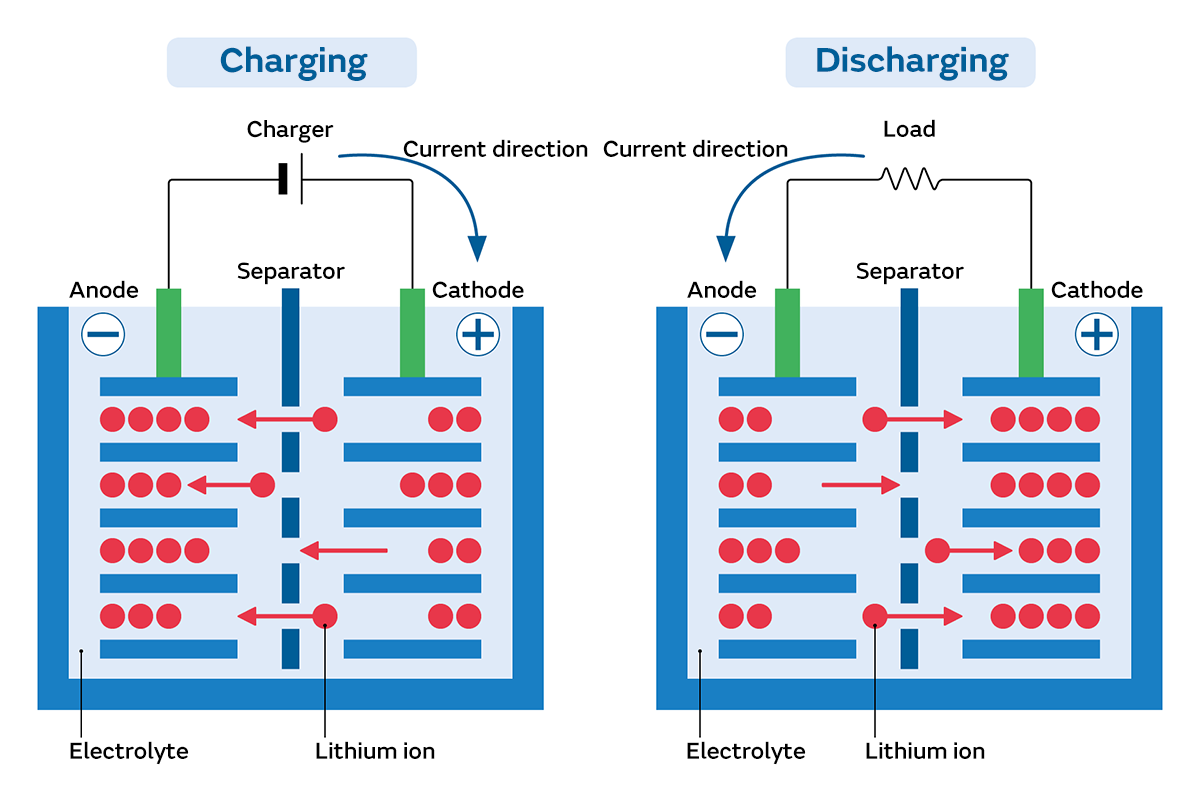
In contrast, secondary batteries facilitate a reversible conversion between electrical and chemical energy. This allows for the battery to be recharged multiple times. Secondary batteries are crucial for applications where reusability is necessary, such as in photovoltaic systems. Examples of secondary batteries include lead-acid batteries and lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in electronic devices like laptops, mobile phones, and digital cameras.
Applications of Batteries
Batteries play a vital role in various aspects of modern life. They are used in portable electronic devices, electric vehicles, renewable energy storage systems, and backup power supplies. The development of advanced battery technologies is crucial for enhancing energy efficiency, reducing environmental impact, and promoting sustainable energy solutions.
Overall, understanding the principles behind battery operation is essential for optimizing their performance, extending their lifespan, and ensuring their safe and efficient use in a wide range of applications.

Source: YouTube
