Source: Wikipedia
Azimuth Angle in Solar Energy
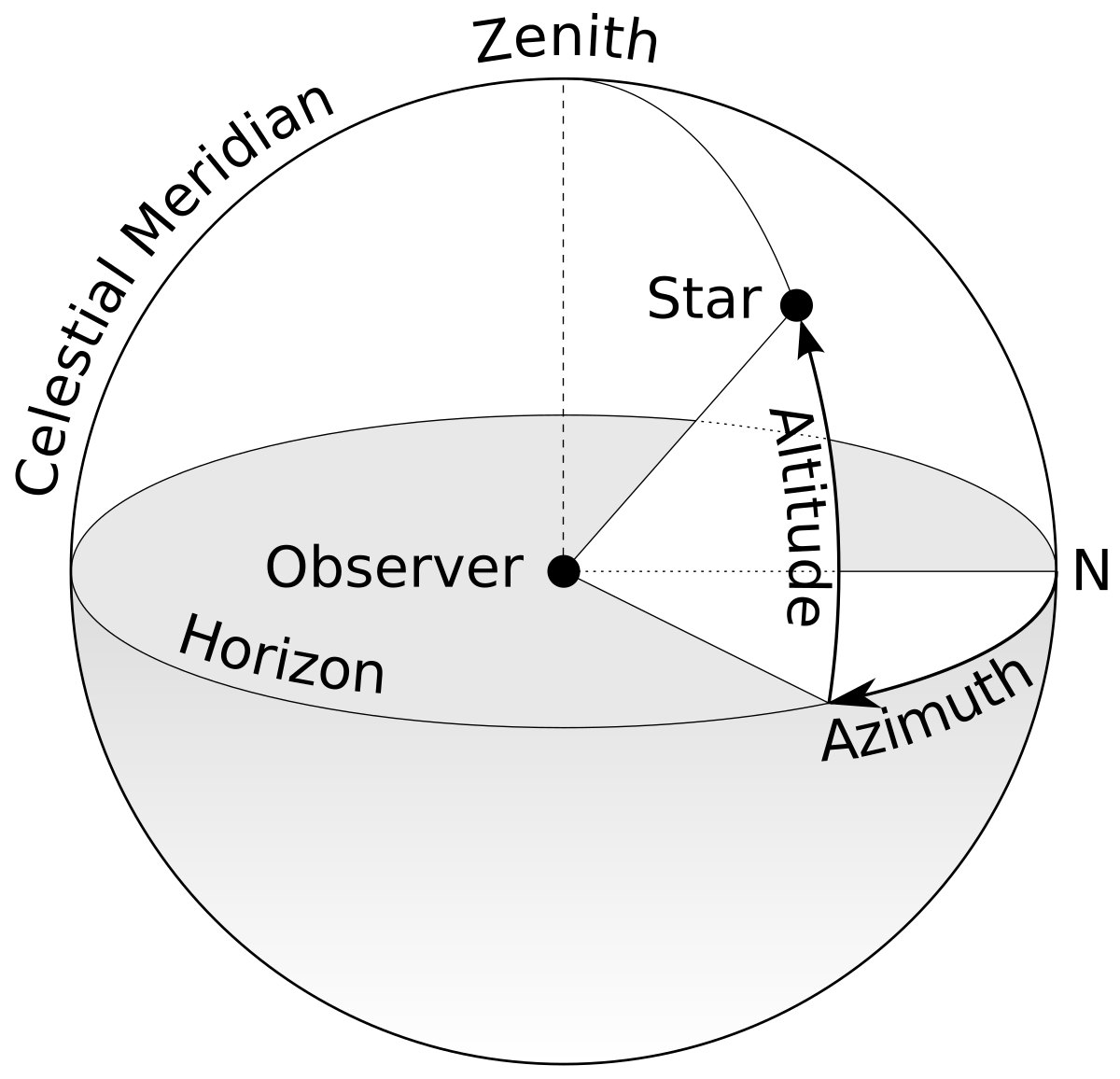
The azimuth angle in solar energy refers to the compass direction from which sunlight is coming. It plays a crucial role in determining the positioning of solar panels to maximize energy absorption. Understanding how the azimuth angle changes throughout the day and across different latitudes is essential for efficient solar energy utilization.
Key Concepts
At solar noon, the sun is directly south in the northern hemisphere and directly north in the southern hemisphere. The azimuth angle varies during the day, with specific values at sunrise and sunset. For instance, at the equinoxes, when the sun rises due east and sets due west, the azimuth angles are 90° and 270°, respectively.
Calculating Azimuth Angle
The azimuth angle can be calculated using the following formula:
Azimuth = cos-1[(sin δ cos Φ – cos δ sin Φ cos(HRA)) / cos α]
Where:
- α: Elevation angle
- Φ: Latitude
- δ: Declination angle
- HRA: Hour angle
This formula provides the correct azimuth angle in the solar morning. Specifically, Azimuth = A zi for Local Solar Time (LST) < 12 or Hour Angle (HRA) < 0.
Significance in Solar Panel Placement
Optimal positioning of solar panels is crucial for maximizing energy production. By considering the azimuth angle based on location and time of day, solar panels can be oriented to receive sunlight most effectively. This alignment ensures that solar panels capture the maximum amount of solar energy throughout the day, enhancing overall energy efficiency.

Source: Go Solar Quotes
Feel free to comment your thoughts.
