Source: MDPI
Understanding PV Array Connections
When setting up a larger photovoltaic (PV) array, it is common to connect individual PV modules in both series and parallel configurations. A series-connected set of solar cells or modules is referred to as a “string”. This combination of series and parallel connections can introduce various challenges in PV arrays.
Effect of Open-Circuit in Series Strings
One potential issue that can arise in PV arrays is an open-circuit in one of the series strings. In such a scenario, the current from the parallel connected string, often called a “block”, will have a lower current compared to the remaining blocks in the module. This situation is akin to having one shaded solar cell in series with several good cells, leading to a loss of power from the entire block of solar cells.
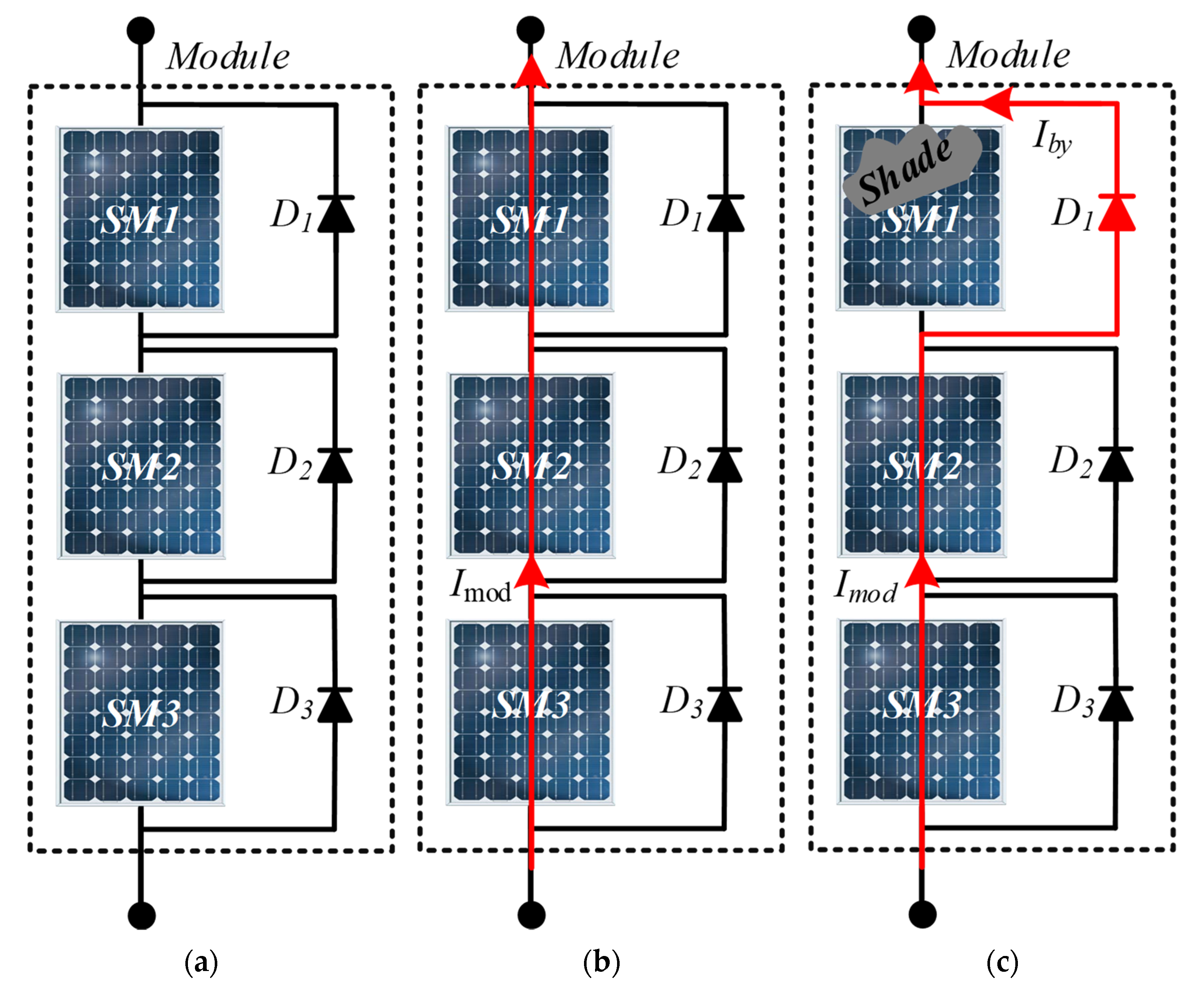
Mismatch Effects and By-pass Diodes
Parallel connections combined with mismatch effects can also cause problems if the by-pass diodes are not rated to handle the current of the entire parallel connected array. For instance, in parallel strings with series connected modules, the by-pass diodes of the series connected modules are connected in parallel. A mismatch in the series connected modules can result in current flowing through a by-pass diode, causing it to heat up. This heating reduces the effective resistance, leading to more current flowing through the slightly hotter set of by-pass diodes. This cycle continues, potentially causing damage if the diodes are not rated for the current.
Role of Blocking Diodes
Aside from using by-pass diodes to mitigate mismatch losses, blocking diodes can also be employed to minimize such losses. A blocking diode, typically used to prevent the module from loading the battery at night, stops current flow from the battery through the PV array. When using parallel connected modules, each string connected in parallel should have its own blocking diode. This not only reduces the required current carrying capability of the blocking diode but also prevents current from flowing between parallel strings of different currents, thereby helping to minimize mismatch losses in parallel connected arrays.
