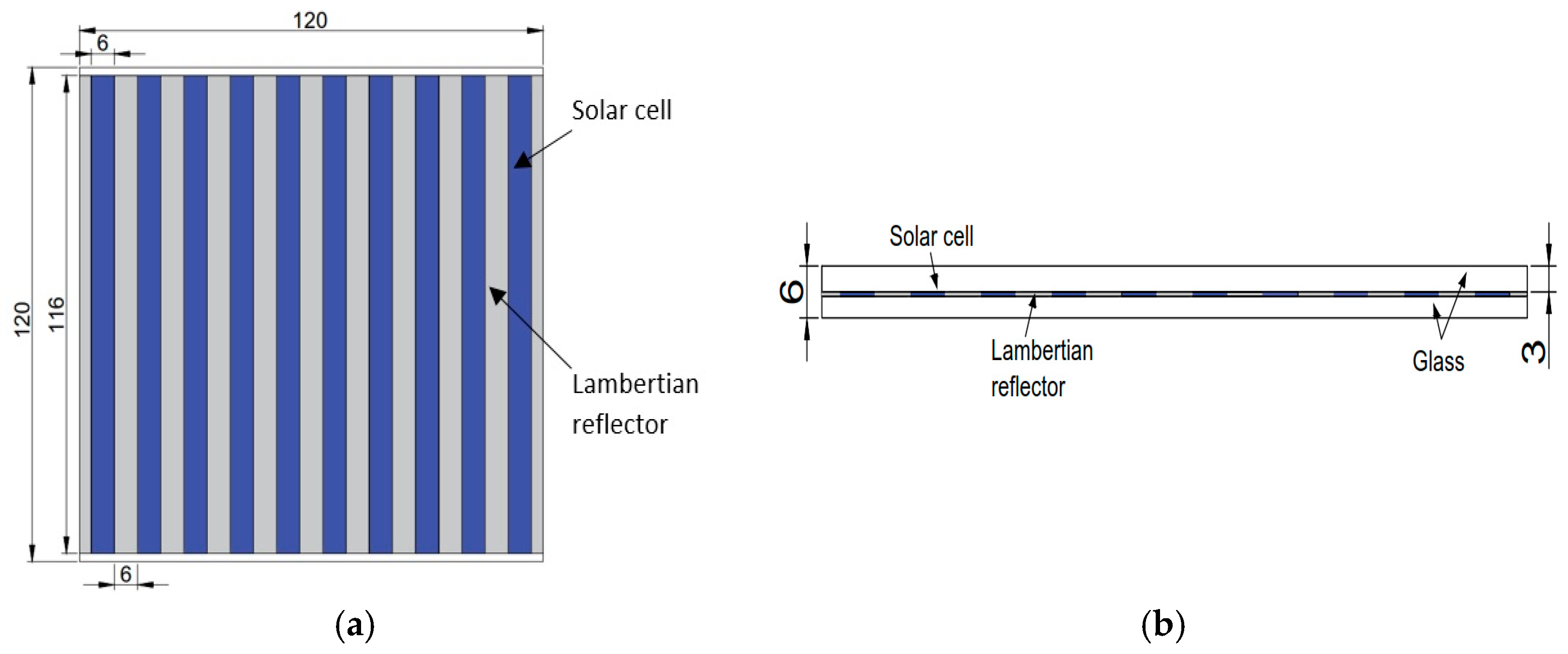
Source: MDPI
Lambertian Back Reflector in Solar Cells
A Lambertian back reflector is a specialized type of rear reflector that scatters the reflected light in various directions. This scattering helps in reducing absorption in the rear cell contacts or transmission from the rear, enabling the light to bounce back into the cell for potential absorption.
Light Trapping and Reflection
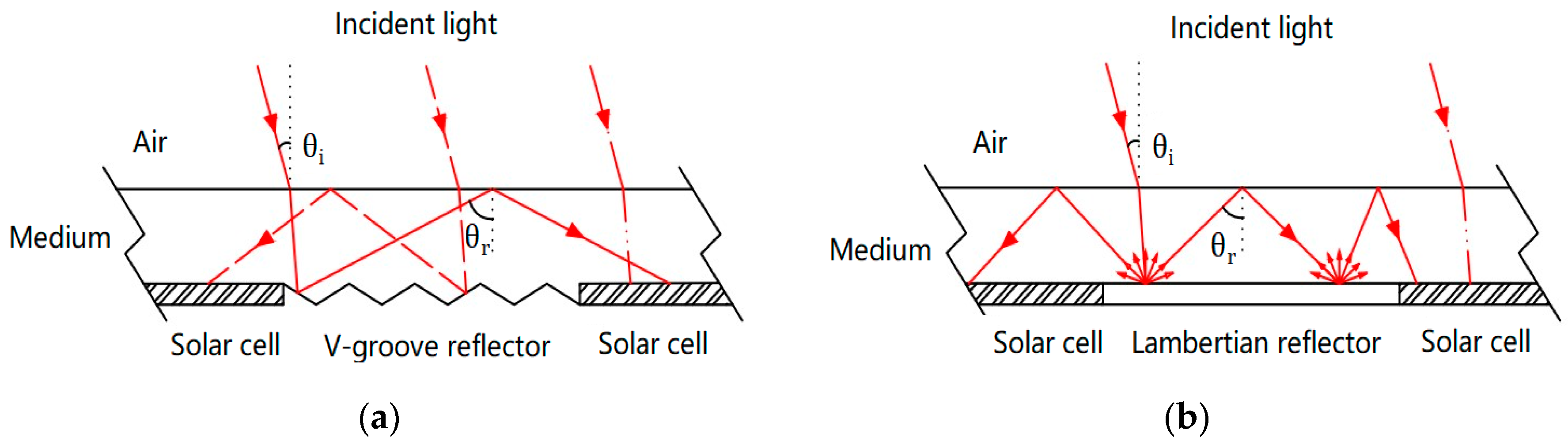
By randomizing the direction of light, a significant portion of the reflected light can undergo total internal reflection. When light reaches the top surface at an angle greater than the critical angle for total internal reflection, it gets reflected towards the back surface. This process can greatly enhance light absorption within the solar cell, effectively increasing the optical path length by a factor of up to 4n^2, where n is the refractive index of the semiconductor material.
This enhancement in light trapping allows for an optical path length approximately 50 times the physical thickness of the device, making it a highly efficient light trapping technique.
Effects on Solar Cell Performance
The implementation of a Lambertian back reflector can significantly improve the performance of a solar cell. By increasing the path length of light within the cell, more photons are absorbed, leading to higher short-circuit currents. In contrast, without effective light trapping, a portion of incident light may pass through the cell without being absorbed, resulting in lower overall efficiency.
The level of light trapping achieved in practice lies between the ideal scenario and no light trapping at all, impacting the overall efficiency and performance of the solar cell.
Overall, the use of Lambertian back reflectors plays a crucial role in enhancing the optical properties of solar cells and improving their energy conversion efficiency.
Source: MDPI
