
Source: YouTube
Understanding Photons: Energy and Wavelength Relationship
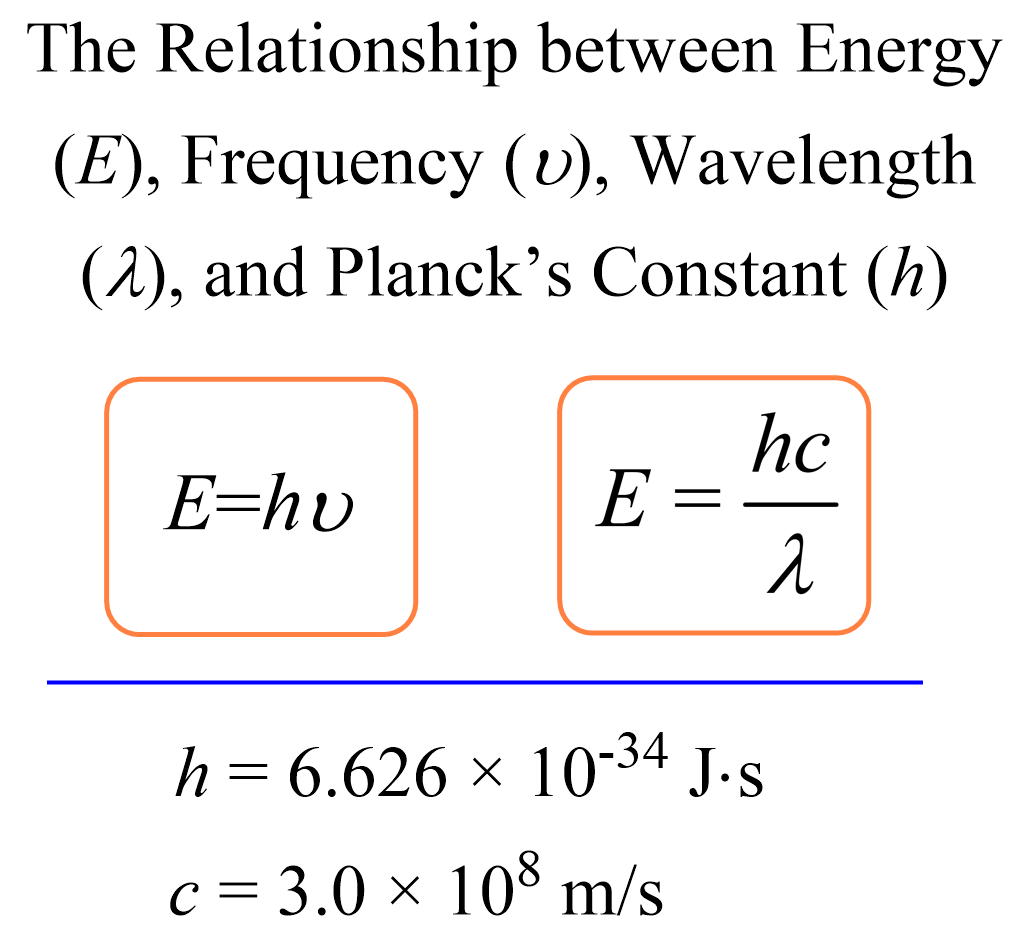
Photons, the fundamental particles of light, can be characterized by their energy or wavelength. This relationship is governed by Planck’s constant (h) and the speed of light (c).
Energy-Wavelength Relationship
The energy of a photon (E) is inversely proportional to its wavelength (λ), as described by the equation E = hc/λ, where h is Planck’s constant and c is the speed of light.
For high-energy photons like “blue” light, the wavelength is short, while low-energy photons like “red” light have longer wavelengths.
Units of Energy
When dealing with photons, the electron-volt (eV) is commonly used as a unit of energy. 1 eV is equivalent to 1.602 × 10^-19 joules. By converting the constant hc into eV-m, we can relate energy to wavelength more conveniently.
Common Expression
Expressing photon energy in terms of eV and µm (micrometers) yields the commonly used equation E(µm) = 1.24/λ(µm), where E is the energy of the photon and λ is the wavelength in micrometers.
The approximate value of 1.24 is often used for simplification in calculations related to photon energy and wavelength.
To determine the energy of a photon at a specific wavelength, the equation E(µm) = 1.24/λ(µm) can be utilized.
Source: Chemistry Steps
Feel Free to comment your thoughts.
